Quick Summary
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery offers enhanced precision through 3D visualization, tremor filtration, and improved instrument dexterity compared to conventional laparoscopic surgery. According to ASMBS 2024 research, both approaches achieve similar weight loss outcomes (60-70% excess weight loss), with robotic surgery showing slightly shorter hospital stays but longer operative times and higher costs. The choice depends on surgeon expertise, patient complexity, and facility availability rather than significant outcome differences.
Why Trust This Guide
This guide synthesizes current research from the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), the International Federation for Surgery of Obesity (IFSO), and peer-reviewed studies published in Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases and Obesity Surgery journals. Our content reflects 2024-2025 clinical evidence comparing robotic and laparoscopic bariatric approaches.
Carely Clinic’s bariatric team maintains ongoing education in both surgical platforms to provide patients with evidence-based recommendations tailored to individual circumstances.
What Is Robotic Gastric Sleeve Surgery?
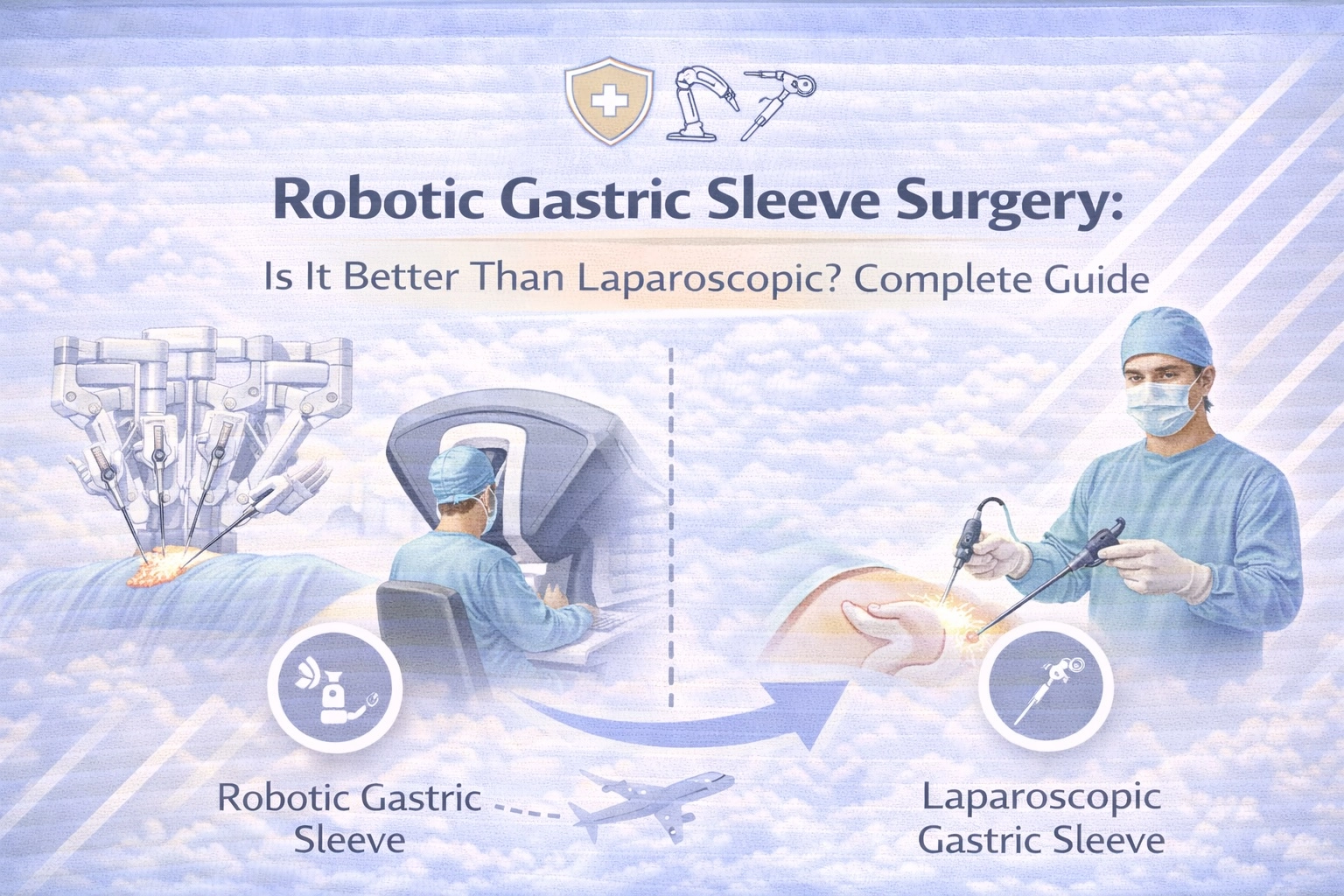
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery uses computer-assisted robotic platforms like the da Vinci Surgical System to perform sleeve gastrectomy, removing approximately 75-80% of the stomach to create a tube-shaped sleeve that reduces food intake and hunger hormones.
The surgeon controls robotic arms from a console while viewing a magnified 3D image of the surgical field. Unlike autonomous robots, the system translates the surgeon’s hand movements into precise instrument movements inside the patient’s body. The da Vinci platform provides seven degrees of freedom in instrument movement, compared to four degrees with standard laparoscopic instruments.
Gastric sleeve surgery—whether performed robotically or laparoscopically—remains fundamentally the same procedure. The stomach is divided vertically using surgical staplers, and the larger curved portion is removed permanently. The remaining sleeve holds approximately 2-3 ounces of food, compared to the original capacity of 40-50 ounces.
The first robotic bariatric procedure was performed in 1999, and adoption has accelerated significantly since 2015. According to MBSAQIP database analysis, robotic sleeve gastrectomy increased from approximately 6.7% of all sleeve procedures in 2015 to 29.5% by 2022, reflecting growing surgeon familiarity with the technology.
Robotic vs Laparoscopic: Key Differences
The primary difference between robotic and laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery is the surgical interface—robotic platforms provide enhanced visualization, tremor filtration, and articulating instruments, while laparoscopic surgery uses direct handheld instruments with 2D visualization.
Both approaches are minimally invasive, using small incisions and specialized instruments to access the abdominal cavity. Neither requires large open incisions, and both typically involve 4-6 small port sites for instrument access. However, the technology through which surgeons manipulate these instruments differs substantially.
Visualization Differences
Laparoscopic surgery uses a camera inserted through one port, displaying a 2D image on a screen positioned away from the operating table. The surgeon must mentally translate this flat image while manipulating instruments at angles that may feel counterintuitive.
Robotic systems provide stereoscopic 3D visualization with up to 10x magnification. The surgeon views this image through a console that aligns their eyes and hands in a natural orientation, reducing the cognitive translation required during laparoscopy.
Instrument Control
Standard laparoscopic instruments are rigid and straight, with movement limited to four degrees of freedom. The abdominal wall acts as a fulcrum, creating a “mirror effect” where moving the handle right causes the instrument tip to move left.
Robotic instruments feature EndoWrist technology, allowing them to bend and rotate with seven degrees of freedom—mimicking and exceeding natural wrist movement. The system also scales motion (large hand movements become small instrument movements) and filters physiological hand tremors.
Surgeon Positioning
During laparoscopic surgery, surgeons stand at the operating table, often for hours in ergonomically challenging positions. This can contribute to surgeon fatigue, particularly in patients with obesity where thick abdominal walls require significant force to manipulate instruments.
Robotic surgery allows surgeons to operate from a seated position at a console, potentially reducing fatigue and improving precision during lengthy procedures. However, this physical separation from the patient requires careful team coordination and immediate availability of a bedside assistant.
Comparison of Outcomes
Both robotic and laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery achieve equivalent weight loss outcomes, with most studies showing 60-70% excess weight loss at one year regardless of surgical approach.
A comprehensive 2024 analysis from the American Journal of Surgery examined over 69,000 sleeve gastrectomy procedures and found that when accounting for stapler technology used, patient outcomes following robotic and laparoscopic approaches were equivalent. The study noted that earlier research showing differences may have been confounded by variations in surgical equipment rather than the robotic platform itself.
Research presented at the ASMBS 2024 Annual Scientific Meeting demonstrated that total robotic sleeve gastrectomy produced operative times of 47.4 minutes compared to 56.9 minutes for laparoscopic approaches in a single-surgeon comparison of 809 procedures. However, this finding reflects one surgeon’s extensive robotic experience and may not generalize to all practitioners.
Weight Loss Results
Long-term weight loss outcomes appear equivalent between approaches. Patients typically achieve 50-70% excess weight loss at one year, 60-70% at two years, and maintain approximately 50-55% excess weight loss at ten years. These results depend primarily on patient adherence to dietary and lifestyle modifications rather than the surgical platform used.
A prospective five-year study found mean excess weight loss of 82% at one year and 60.3% at five years following laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy—outcomes that mirror results reported for robotic procedures in comparable patient populations.
Hospital Stay and Recovery
Several studies suggest robotic surgery may be associated with slightly shorter hospital stays. A 2024 MBSAQIP analysis found reduced length of stay with robotic approaches, though the clinical significance of a difference measured in hours remains debatable.
Recovery timelines following either approach are similar. Most patients return to desk work within 1-2 weeks, resume normal activities at 4-6 weeks, and reach full recovery by 3-6 months. The minimally invasive nature of both techniques means neither requires the extended recovery associated with open surgery.
Advantages of Robotic Surgery
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery offers enhanced surgical precision through 3D visualization, tremor filtration, and articulating instruments that may benefit complex cases or surgeons transitioning from open to minimally invasive techniques.
Superior Visualization
The robotic platform’s 3D high-definition display provides depth perception absent in standard laparoscopy. Surgeons report that this enhanced visualization makes tissue identification easier, particularly when dissecting near critical structures like the spleen or when addressing unexpected adhesions from previous surgeries.
Magnification up to 10x allows detailed viewing of anatomical structures, potentially improving identification of bleeding vessels and ensuring complete visualization during stapling. This may be particularly valuable in patients with high BMI where anatomical landmarks can be obscured by adipose tissue.
Tremor Elimination
The da Vinci system filters out natural hand tremors through sophisticated motion control algorithms. While healthy surgeons typically have minimal tremor, even slight hand movement becomes magnified when translated through long laparoscopic instruments. Robotic tremor filtration ensures steady instrument positioning regardless of subtle surgeon movements.
This precision proves valuable during tasks requiring fine motor control, such as suturing, tissue handling near delicate structures, and staple line reinforcement. The technology essentially creates “rock-steady precision that’s impossible to achieve manually,” according to surgical platform documentation.
Improved Ergonomics
Surgeons operating from a seated console report reduced physical fatigue compared to standing throughout laparoscopic procedures. This ergonomic benefit may become increasingly relevant as surgical careers extend and as procedures are performed on patients with higher BMI requiring longer operative times.
Some research suggests reduced surgeon fatigue could translate to improved performance during the final portions of lengthy procedures, though direct evidence linking ergonomics to patient outcomes in bariatric surgery remains limited.
Enhanced Articulation
The seven degrees of freedom provided by robotic instruments allow surgeons to approach tissues from angles impossible with rigid laparoscopic tools. This articulation proves particularly valuable in confined spaces and when suturing at difficult angles.
For gastric sleeve surgery specifically, this enhanced dexterity facilitates precise dissection of the gastroesophageal junction and allows for hand-sewn reinforcement of the staple line in surgeons who prefer this technique over stapling alone.
Limitations of Robotic Surgery
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery involves significantly higher costs, longer operative times in less experienced hands, loss of tactile feedback in current-generation systems, and dependence on technology that can malfunction.
Higher Costs
The da Vinci surgical system costs $1-2.5 million per unit, with annual maintenance fees of approximately 20% of purchase price. Additionally, robotic instruments are semi-disposable, requiring replacement after a limited number of uses—typically 10-14 procedures per instrument.
A cost analysis presented at a SAGES meeting found average total costs of $15,319 for robotic bariatric procedures compared to $8,955 for laparoscopic approaches—a difference of over $6,000 per case. These higher costs are passed to patients or healthcare systems without clear evidence of proportionally improved outcomes for straightforward sleeve gastrectomy.
In the United States and Canada, robotic-assisted bariatric surgery can cost upwards of $40,000, compared to $15,000-25,000 for standard laparoscopic procedures. This cost differential raises questions about value in healthcare systems facing budget constraints.
Longer Operative Times
While experienced robotic surgeons may achieve comparable or even shorter operative times, the learning curve for robotic surgery is significant. Setup and docking of the robotic system adds time before surgery begins, and surgeons new to the platform typically have longer procedures.
A comprehensive review found that robotic surgery frequently requires more time in the operating room than laparoscopic approaches, particularly early in a surgeon’s robotic experience. Extended operative times potentially increase anesthesia-related risks and reduce operating room efficiency.
Loss of Tactile Feedback
Current-generation robotic systems (prior to the da Vinci 5) lack haptic feedback—the surgeon cannot feel tissue tension, resistance, or texture. Experienced laparoscopic surgeons rely heavily on tactile information to gauge stapling pressure, identify tissue planes, and sense abnormalities.
While visual cues can partially compensate, the absence of touch sensation requires surgeons to develop new techniques for tissue handling. The newest da Vinci 5 model introduces “Force Feedback” technology, though this system is not yet widely deployed.
Technology Dependence
Robotic surgery creates dependence on complex technology that can malfunction. System errors, power failures, or mechanical issues can occur mid-procedure, potentially requiring conversion to laparoscopic or open approaches. While such events are rare, they require contingency planning and backup capabilities.
The physical separation of surgeon from patient during robotic surgery also means that bedside assistants must be prepared to intervene rapidly if complications arise. Team coordination becomes essential in ways that differ from direct laparoscopic surgery.
Who Benefits Most from Robotic Approach?
Patients with very high BMI (≥50), those requiring revisional surgery, and individuals with complex anatomy may derive greater benefit from robotic platforms, though evidence remains mixed.
Super-Obese Patients
Patients with BMI ≥50 kg/m² present technical challenges including thick abdominal walls, enlarged livers, and reduced working space. Some surgeons report that robotic instruments better handle these challenges by reducing the physical strain of instrument manipulation through dense tissue.
A study examining robot-assisted sleeve gastrectomy in morbidly obese versus super-obese patients found no significant difference in operative time, blood loss, or complications between groups—suggesting that robotic technology may attenuate the increased difficulty typically seen in higher-BMI patients.
Revisional Bariatric Surgery
Patients requiring conversion from previous bariatric procedures (such as gastric band removal with sleeve conversion) face altered anatomy, scar tissue, and adhesions. The precision of robotic platforms may offer advantages in these technically demanding cases.
Research on revisional bariatric surgery suggests the robotic approach shows fewer complications, shorter hospital stays, and reduced need for conversion to open surgery compared to laparoscopic revisional procedures. This represents one area where robotic advantages appear more clearly established.
Complex Medical History
Patients with previous abdominal surgeries, anatomical variations, or medical conditions requiring careful tissue handling may benefit from enhanced visualization and instrument control. The surgeon’s ability to assess three-dimensional tissue relationships and apply precise force becomes more valuable when navigating around adhesions or abnormal structures.
Surgeon Training Considerations
Surgeons transitioning from open to minimally invasive surgery may find the robotic platform easier to learn than traditional laparoscopy. The intuitive instrument control and natural hand-eye orientation reduce the counterintuitive adjustments required for laparoscopic technique.
Studies suggest the learning curve for robotic gastric bypass may be shorter than for laparoscopic approaches, though this finding requires validation for sleeve gastrectomy specifically and across different training backgrounds.
Safety and Complication Rates
Both robotic and laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery are remarkably safe, with mortality rates of 0.08% (approximately 8 per 10,000 procedures) and major complication rates of 1-2%—comparable to gallbladder removal surgery.
Overall Safety Profile
Gastric sleeve surgery—regardless of approach—carries mortality and complication rates lower than many commonly performed procedures. According to ASMBS data, the 30-day mortality rate for sleeve gastrectomy is 0.08%, compared to 0.14% for gastric bypass and rates associated with routine gallbladder and hip replacement surgeries.
The 30-day serious complication rate for sleeve gastrectomy is approximately 0.96%, including leak rates of 0.3%. These figures reflect the overall safety of the procedure rather than differences between robotic and laparoscopic approaches.
Comparative Complication Data
A 2024 retrospective analysis of over 800,000 cases from the MBSAQIP database found that robotic sleeve gastrectomy had slightly higher complication rates compared to laparoscopic approaches, though outcomes have become more similar over time as robotic technology and surgeon experience have improved.
Conversely, some single-surgeon series report lower complication rates (1.7% vs 5.1%) with total robotic approaches, highlighting the importance of surgeon volume and expertise regardless of platform. The conflicting findings underscore that surgical skill likely matters more than technology selection for straightforward cases.
Leak Rates
Staple line leak represents the most serious complication of sleeve gastrectomy. Published leak rates range from 0.3% to 1.2% regardless of surgical approach. Neither robotic nor laparoscopic technique has demonstrated a clear advantage in preventing this complication.
Expert Insight
“The safety profile of laparoscopic bariatric procedures compares positively with other common procedures at 30 days. Both robotic and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy achieve excellent safety profiles when performed at accredited centers.”
— Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases, 2024
Bleeding Complications
Some studies suggest robotic surgery may be associated with lower rates of bleeding and transfusion requirements, potentially due to enhanced visualization and precise tissue handling. However, these findings are not consistent across all research, and bleeding complications remain rare with both approaches.
Cost Comparison
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery costs $3,000-$6,000 more than laparoscopic approaches in most healthcare systems, with prices varying significantly by country and facility.
United States Pricing
In the United States, standard laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery typically costs $15,000-$25,000, while robotic-assisted procedures can cost $40,000 or more depending on facility and insurance coverage. Insurance coverage varies, with some plans covering bariatric surgery when medically necessary criteria are met.
The cost differential reflects equipment acquisition, maintenance, and disposable instrument expenses associated with robotic platforms. These costs are generally passed to patients or insurers without clear evidence of proportionally improved outcomes.
International Comparison
| Country | Laparoscopic Sleeve | Robotic Sleeve | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | $15,000-$25,000 | $25,000-$40,000+ | Insurance may cover |
| United Kingdom | £8,000-£15,000 | £12,000-£20,000 | NHS limited availability |
| Turkey | €2,500-€5,500 | €4,000-€7,500 | All-inclusive packages |
| Mexico | $4,000-$7,000 | $8,000-$12,000 | Limited robotic availability |
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Current evidence does not support the additional expense of robotic surgery for straightforward primary sleeve gastrectomy in average-risk patients. The technological advantages may not translate to measurably improved outcomes that justify the cost differential.
However, for complex cases—revisional surgery, super-obese patients, or procedures requiring extensive suturing—the cost-benefit calculation may favor robotic approaches if complication rates or conversion to open surgery can be reduced.
How This Applies in Turkey
International guidelines from ASMBS and IFSO apply equally at Turkey’s JCI-accredited facilities, with both robotic and laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery available at leading Istanbul hospitals following identical clinical protocols as American and European institutions.
The key differences for international patients are cost and accessibility. Laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery in Turkey costs €2,500-€5,500 all-inclusive, compared to $15,000-$25,000 in the USA and £8,000-£15,000 in the UK—representing savings of 60-75%. Robotic approaches are available at select centers including Memorial Hospital, Anadolu Medical Center, and Acıbadem for patients specifically requesting this technology.
Most bariatric surgery in Turkey is performed laparoscopically with excellent outcomes. Turkish surgeons have extensive experience with minimally invasive techniques, and the laparoscopic approach remains the standard of care for primary sleeve gastrectomy. Robotic surgery is typically reserved for revisional procedures or upon patient request.
At Carely Clinic in Istanbul, gastric sleeve surgery is performed by board-certified bariatric surgeons at JCI-accredited partner hospitals. All-inclusive packages include pre-operative evaluation, surgery, hospital stay, medications, accommodation, transfers, and post-operative follow-up. International patients typically complete the entire process within 5-7 days.
Learn more about Gastric Sleeve Surgery at Carely Clinic.
Summary Comparison Table
| Factor | Robotic Sleeve | Laparoscopic Sleeve |
|---|---|---|
| Weight Loss | 60-70% EWL at 1 year | 60-70% EWL at 1 year |
| Mortality Rate | 0.08% | 0.08% |
| Major Complication Rate | 1-2% | 1-2% |
| Operative Time | 45-90 minutes | 45-75 minutes |
| Hospital Stay | 1-2 nights | 1-2 nights |
| Visualization | 3D HD, 10x magnification | 2D HD |
| Tremor Filtration | Yes | No |
| Instrument Articulation | 7 degrees of freedom | 4 degrees of freedom |
| Tactile Feedback | Limited (newest models improved) | Yes |
| Cost (Turkey) | €4,000-€7,500 | €2,500-€5,500 |
| Cost (USA) | $25,000-$40,000+ | $15,000-$25,000 |
| Best For | Revisional surgery, BMI ≥50, complex cases | Primary surgery, standard cases |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is robotic gastric sleeve surgery safer than laparoscopic?
No, both approaches have equivalent safety with 0.08% mortality rates and 1-2% major complications. Large database studies show no significant difference in safety between robotic and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy at accredited bariatric centers. The surgeon’s experience and the facility’s accreditation matter more than the technology used.
Will I lose more weight with robotic surgery?
No, weight loss outcomes are equivalent at 60-70% excess weight loss at one year. Both robotic and laparoscopic gastric sleeve surgery achieve similar long-term results. Weight loss depends on adherence to dietary guidelines, exercise, and lifestyle modifications rather than the surgical platform used.
Does robotic surgery have a faster recovery?
No, recovery timelines are nearly identical between robotic and laparoscopic approaches. Some studies show robotic surgery may reduce hospital stay by several hours, but the practical difference is minimal. Most patients return to desk work within 1-2 weeks and normal activities within 4-6 weeks regardless of approach.
Why is robotic surgery more expensive?
Robotic surgery costs $3,000-$6,000 more due to equipment costs, maintenance fees, and semi-disposable instruments. The da Vinci system costs $1-2.5 million, with annual maintenance fees at 20% of purchase price, and instruments requiring replacement every 10-14 uses. These expenses are passed to patients without evidence of proportionally improved outcomes for routine cases.
Should I choose robotic surgery if available?
Surgeon experience matters more than technology for straightforward primary sleeve gastrectomy at accredited facilities. Robotic surgery may offer advantages for revisional procedures, super-obese patients (BMI ≥50), or complex cases with unusual anatomy requiring enhanced visualization and precision.
Is the surgeon still performing the surgery with robotics?
Yes, the surgeon performs the entire procedure—the robot enhances precision but operates under complete surgeon control. The surgeon sits at a console controlling all instrument movements while viewing a 3D image of the surgical field. Every action is directed by the surgeon, not autonomous technology.
How long does robotic gastric sleeve surgery take?
Operative times range 45-90 minutes depending on surgeon experience, plus 15-30 minutes for robotic system setup. Experienced robotic surgeons may achieve times comparable to or shorter than laparoscopic approaches. However, setup and docking of the robotic system adds time before surgery begins.
Are there risks specific to robotic surgery?
Yes, robotic-specific risks include potential equipment malfunction requiring surgical conversion and loss of tactile feedback. Robotic-specific risks include potential equipment malfunction requiring conversion to laparoscopic or open surgery, and the loss of tactile feedback in current-generation systems. These risks are rare and managed by having backup plans and skilled bedside assistants.
Is robotic gastric sleeve available in Turkey?
Yes, robotic surgery is available at Carely Clinic, Memorial Hospital, Anadolu Medical Center, and Acıbadem in Turkey. However, most Turkish bariatric surgeons perform laparoscopic procedures with excellent outcomes, reserving robotic approaches for complex or revisional cases requiring enhanced precision.
How do I decide which approach is right for me?
Discuss with your bariatric surgeon considering BMI, previous surgeries, health status, and cost factors. Factors to consider include your BMI, previous surgeries, overall health status, surgeon recommendation, and cost considerations. For most patients undergoing primary sleeve gastrectomy, an experienced laparoscopic surgeon will achieve excellent results at lower cost.
Conclusion
Robotic gastric sleeve surgery offers enhanced precision through 3D visualization, tremor filtration, and improved instrument articulation, but these technological advantages have not translated to measurably superior outcomes compared to laparoscopic surgery for routine cases. Both approaches achieve mortality rates of 0.08%, major complication rates of 1-2%, and weight loss of 60-70% excess weight at one year.
The choice between robotic and laparoscopic approaches should be individualized based on patient complexity, surgeon expertise, and cost considerations. Robotic technology may offer meaningful advantages for revisional bariatric surgery, super-obese patients, and complex anatomical situations where enhanced visualization and dexterity provide tangible benefits.
For the majority of patients seeking primary gastric sleeve surgery, an experienced laparoscopic surgeon at an accredited bariatric center will deliver excellent results. The surgeon’s volume and experience consistently predict outcomes more reliably than the technology platform used.
Disclaimer: Individual requirements and outcomes vary. This guide provides general information based on current international guidelines and peer-reviewed research. Consult qualified medical professionals for personalized advice regarding surgical approach selection.
Ready to explore your weight loss surgery options? Contact Carely Clinic for a comprehensive consultation with our bariatric surgery team to determine the best approach for your individual circumstances.