Quick Summary
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG) is a non-surgical weight loss procedure that reduces stomach volume by 70-80% using sutures placed through the mouth, achieving 15-20% total body weight loss within one year. The IFSO Bariatric Endoscopy Committee endorses ESG as an effective treatment for Class I and II obesity (BMI 30-40), with a complication rate of just 1.5-2.3% compared to 12-18% for surgical gastric sleeve.
This guide covers ESG eligibility requirements, expected weight loss outcomes, safety profile, recovery timeline, costs by country, and how the procedure compares to surgical alternatives.
Why Trust This Guide
This guide synthesizes evidence from the 2024 IFSO Bariatric Endoscopy Committee Position Statement, the landmark MERIT randomized controlled trial published in The Lancet, and data from over 7,500 ESG patients across multiple meta-analyses. Our content follows peer-reviewed research from Obesity Surgery, Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, and guidelines from leading bariatric institutions including Mayo Clinic, Johns Hopkins Medicine, and Cleveland Clinic.
Carely Clinic’s medical team ensures accuracy through evidence-based review, combining international guideline recommendations with real-world clinical outcomes data.
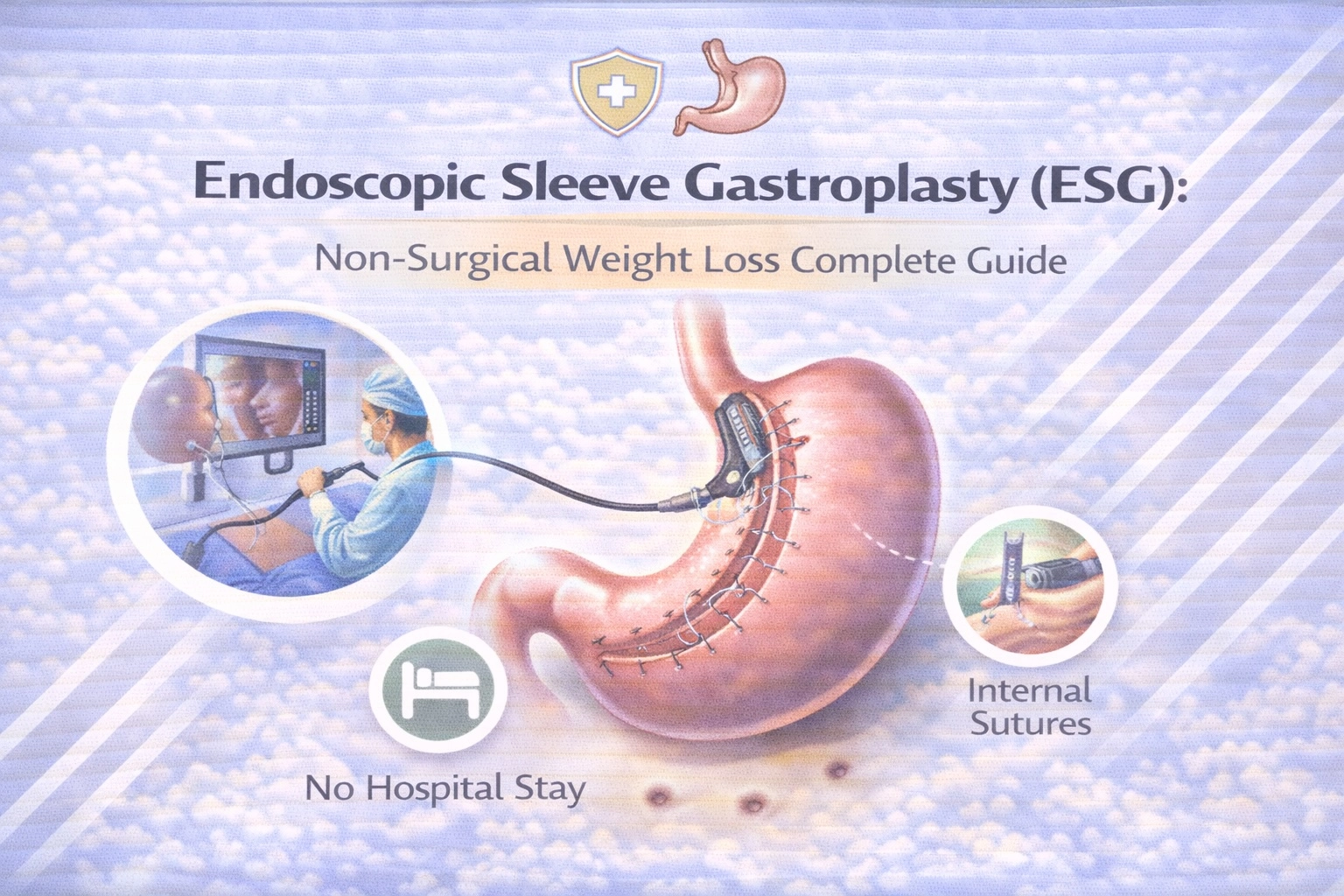
What Is Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty (ESG)?
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty is a minimally invasive, incision-free weight loss procedure that reduces stomach size by approximately 70% using sutures placed through the mouth, without removing any stomach tissue or making external incisions.
Unlike traditional bariatric surgery, ESG accesses the stomach through the esophagus using an endoscope—a flexible tube equipped with a camera and specialized suturing device. The gastroenterologist places a series of full-thickness sutures along the stomach’s greater curvature, folding the tissue accordion-style to create a narrow, tubular sleeve shape similar to what surgical gastric sleeve achieves, but without permanent anatomical changes.
The procedure received FDA authorization in July 2022, making it the first endoscopic suturing device cleared specifically for obesity management. According to the IFSO Bariatric Endoscopy Committee’s 2024 position statement, ESG fills a critical gap for patients who cannot undergo or prefer to avoid traditional metabolic and bariatric surgery (MBS), particularly those with Class I and II obesity who often don’t meet conventional surgical BMI thresholds.
ESG is sometimes called the “accordion procedure” due to how the sutures create accordion-like folds. The stomach retains normal digestive function but holds significantly less food, promoting earlier satiety and delayed gastric emptying—two mechanisms that drive sustained weight loss.
How Does ESG Work?
ESG works by physically reducing stomach capacity and slowing gastric emptying through a series of full-thickness sutures that reshape the stomach into a narrow tube, decreasing volume from approximately 1500ml to 400-500ml.
The Procedure Step-by-Step
The ESG procedure typically takes 60-90 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia as an outpatient procedure. Here’s what happens during treatment:
Pre-Procedure Preparation: Patients fast for at least 8 hours before the procedure. No bowel preparation is required, unlike some other endoscopic procedures.
Endoscope Insertion: The gastroenterologist inserts the endoscope—a flexible tube with a camera and the OverStitch suturing device attached—through the mouth and esophagus into the stomach. Gas is released to expand the stomach for better visualization.
Suture Placement: Using the camera for guidance, the physician places approximately 6-12 full-thickness sutures in a triangular pattern along the stomach’s greater curvature, from the gastric fundus (top) to near the antrum (bottom).
Sleeve Creation: As each suture is tightened, the stomach walls fold inward, creating the characteristic sleeve shape. The stomach’s capacity reduces by 70-80%, leaving a narrow tube that restricts food intake.
Completion: The sutures create permanent folds that are reinforced over time by natural scar tissue formation. The entire digestive pathway remains intact—no part of the stomach is removed, and the connection to the intestines is unchanged.
Mechanisms of Weight Loss
ESG promotes weight loss through multiple mechanisms that work synergistically:
Gastric Restriction: The smaller stomach volume physically limits portion sizes. Patients report feeling satisfied after eating just ¼ to ½ cup of food.
Delayed Gastric Emptying: Studies demonstrate that ESG significantly slows the rate at which food leaves the stomach, prolonging feelings of fullness and reducing hunger between meals.
Early Satiation: The altered stomach shape triggers satiety signals sooner during meals, helping patients stop eating when appropriately full rather than when the plate is empty.
ESG Eligibility Requirements
ESG eligibility requires a BMI of 30 or higher according to FDA approval, though the IFSO endorses ESG for Class I obesity (BMI 30-34.9), Class II obesity (BMI 35-39.9), and even Class III patients (BMI ≥40) who are not suitable candidates for traditional bariatric surgery.
Primary Eligibility Criteria
The fundamental requirements for ESG candidacy include:
BMI Requirements: FDA authorization covers patients with BMI 30-50. Unlike surgical weight loss procedures that typically require BMI ≥35 with comorbidities or BMI ≥40 without, ESG offers earlier intervention for patients with lower-range obesity.
Failed Previous Attempts: Candidates should have a documented history of unsuccessful weight loss through diet, exercise, and lifestyle modifications alone.
Commitment to Lifestyle Change: ESG is a tool, not a cure. Long-term success requires permanent healthy eating habits, regular physical activity, and adherence to post-procedure nutritional guidelines.
No Contraindications: Patients must be medically cleared for general anesthesia and not have conditions that would prevent safe endoscopic access.
Who Is NOT a Candidate for ESG?
Certain conditions disqualify patients from ESG:
- Large hiatal hernia (greater than 3 centimeters)
- Previous gastric surgery or anatomical abnormalities
- Active stomach ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding
- Bleeding disorders or anticoagulant therapy that cannot be paused
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Barrett’s esophagus or severe GERD unresponsive to treatment
- Crohn’s disease affecting the upper GI tract
ESG Eligibility Checklist
| Criterion | Requirement | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| BMI Range | 30-50 kg/m² | FDA-approved range; some centers accept BMI 27+ with comorbidities |
| Age | 18+ years (adults) | IFSO also supports ESG in adolescents with Class II obesity |
| Prior Weight Loss Attempts | Documented history | Failed diet, exercise, or pharmacotherapy |
| Hiatal Hernia | Less than 3 cm | Large hernias contraindicate ESG |
| Previous Gastric Surgery | None (most cases) | ESG may be used for revision of stretched surgical sleeve |
| Anesthesia Clearance | Required | Standard pre-operative evaluation |
| Active GI Disease | None present | Ulcers, bleeding, or inflammatory conditions must be resolved |
Expert Insight
“ESG is particularly beneficial for patients with Class I and II obesity, as well as for those with Class III obesity who are not suitable candidates for metabolic bariatric surgery. The procedure provides significant weight loss outcomes with a favorable safety profile.”
— IFSO Bariatric Endoscopy Committee Position Statement, 2024
Expected Weight Loss Results
ESG patients typically achieve 15-20% total body weight loss (TBWL) within the first year, with studies showing 83% of patients achieving greater than 10% TBWL and results maintained for at least 5 years in prospective follow-up.
Short-Term Results (0-12 Months)
Weight loss after ESG follows a predictable pattern with most reduction occurring in the first six months:
Month 1-3: Patients experience rapid initial weight loss of approximately 10-14% TBWL as they adapt to smaller portions and the post-procedure diet protocol.
Month 3-6: Weight loss continues steadily, with most patients reaching 15-17% TBWL by the six-month mark. This is when approximately 90% of total weight loss typically occurs.
Month 6-12: The rate of loss slows as the body adapts. By 12 months, average TBWL reaches 15.6-17.1%, equivalent to approximately 50-60% excess weight loss (EWL).
Long-Term Durability (1-5+ Years)
Perhaps the most important question for any weight loss intervention is durability. Research demonstrates ESG provides lasting results:
2-Year Outcomes: A large US cohort study of 1,506 patients showed mean TBWL of 15.3% maintained at 24 months, with 69.9% of patients sustaining greater than 10% TBWL.
5-Year Outcomes: Prospective data published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology followed 216 patients for five years, reporting mean TBWL of 15.9% at the five-year mark—remarkably similar to one-year results. Ninety percent maintained at least 5% TBWL, and 61% maintained greater than 10% TBWL at five years.
10-Year Data: Emerging data presented at the American College of Gastroenterology 2024 meeting suggests ESG effectiveness extends to at least 10 years, though long-term studies with larger sample sizes are still ongoing.
Comorbidity Improvement
Beyond weight loss, ESG significantly improves obesity-related health conditions:
- Type 2 Diabetes: Resolution or improvement in 55-66% of patients
- Hypertension: Resolution or improvement in 51-66% of patients
- Dyslipidemia: Resolution in approximately 56% of patients
- Sleep Apnea: Significant improvement in over 50% of patients
- Fatty Liver Disease: Measurable reduction in liver fat content
Expert Insight
“Adherence to follow-up visits is a significant predictor of successful weight loss outcomes after ESG. Regular monitoring by a multidisciplinary team nurtures weight loss, resolution or improvement of comorbidities, and improvement of quality of life.”
— SOFFCOMM Position Statement on ESG, 2025
Is ESG Safe? Risks and Complications
ESG demonstrates an excellent safety profile with serious adverse event rates of just 0.2-2% and no mortality in major studies, making it significantly safer than surgical gastric sleeve while still achieving meaningful weight loss.
Safety Statistics
The safety data from multiple large-scale studies and meta-analyses consistently shows:
Overall Complication Rate: 1.5-2.3% for serious adverse events (Clavien-Dindo Grade III or higher)
Comparison to Surgery: ESG shows a four-fold decrease in complications compared to laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Surgical gastric sleeve carries a 12-18% total complication rate versus approximately 1% for ESG.
Mortality Rate: No deaths reported in the MERIT trial or subsequent major studies. By comparison, surgical gastric sleeve has a mortality rate of 0.03-0.1%.
Common Side Effects
Most patients experience temporary side effects that resolve within days:
- Nausea: Occurs in approximately 10% of patients, typically managed with prescription anti-nausea medication
- Abdominal Pain/Cramping: Common in the first 2-3 days; described as mild discomfort from gas and suture tension
- Burping: About 5% experience frequent burping for 1-2 months
- Sore Throat: Temporary irritation from endoscope passage
Serious Complications (Rare)
While uncommon, potential serious complications include:
- Bleeding: Perioperative GI bleeding occurs in approximately 1.8% of cases; typically managed endoscopically
- Perforation: Extremely rare; most cases are microperforations managed with antibiotics
- Perigastric Fluid Collection: Occasionally identified on imaging; usually resolves with conservative treatment
- Suture Loosening: May occur over time in some patients; can be addressed with repeat endoscopic procedure
ESG vs Surgical Safety Comparison
| Safety Metric | ESG | Gastric Sleeve Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Serious Adverse Events | 1.5-2.3% | 12-18% |
| Mortality Rate | ~0% | 0.03-0.1% |
| New-Onset GERD | Negligible | 15-30% |
| Staple Line Leak | N/A (no staples) | 1-3% |
| Hospital Stay | Same-day discharge | 1-2 nights |
ESG vs Gastric Sleeve Surgery: Complete Comparison
The main difference between ESG and surgical gastric sleeve is that ESG reduces stomach size using internal sutures with no incisions, while gastric sleeve permanently removes 75-80% of the stomach through laparoscopic surgery—resulting in greater weight loss for surgery but higher complication rates.
Procedure Differences
ESG (Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty):
- Non-surgical; performed through the mouth
- No external incisions or scars
- Stomach is folded with sutures, not removed
- Potentially reversible
- 60-90 minute outpatient procedure
- Same-day discharge
Gastric Sleeve (Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy):
- Surgical procedure requiring abdominal incisions
- Permanently removes 75-80% of stomach tissue
- Irreversible anatomical change
- 1-2 hour procedure
- 1-2 night hospital stay required
Weight Loss Comparison
Studies consistently show surgical gastric sleeve achieves greater weight loss, but the difference narrows at higher BMIs:
At 12 Months:
- ESG: 15-18% TBWL (60-77% EWL)
- Gastric Sleeve: 23-29% TBWL (80-95% EWL)
At 24-36 Months:
- ESG: 15-17% TBWL
- Gastric Sleeve: 20-25% TBWL
Important Finding: A propensity score-matched study of over 6,000 patients demonstrated that ESG achieved “noninferior” weight loss to surgical sleeve, particularly in patients with BMI under 40. The mean difference in weight loss was within the 10% noninferiority margin at all follow-up timepoints.
Who Should Choose ESG vs Surgery?
Choose ESG If You:
- Have Class I or II obesity (BMI 30-40)
- Prefer a non-surgical approach
- Cannot tolerate the risks of surgery
- Need faster recovery (work, family obligations)
- Want a reversible option
- Are concerned about GERD (acid reflux)
Choose Surgical Gastric Sleeve If You:
- Have Class III obesity (BMI ≥40)
- Need maximum possible weight loss
- Have severe obesity-related comorbidities requiring aggressive intervention
- Understand and accept surgical risks
- Can accommodate 4-6 week recovery
ESG Recovery Timeline
Most ESG patients return to normal activities within 2-3 days and work within 1 week, with full dietary recovery taking 4-6 weeks as patients progress from liquids to solid foods in a staged protocol.
Day-by-Day Recovery
Procedure Day (Day 0):
- Rest in recovery room for 2-3 hours post-procedure
- May experience grogginess from anesthesia
- Begin sipping clear liquids once cleared
- Discharge home with caretaker the same day
Days 1-2:
- Clear liquid diet (water, broth, sugar-free gelatin, clear protein drinks)
- Mild nausea and abdominal discomfort common; managed with prescribed medications
- Rest recommended; light walking encouraged to prevent blood clots
- Take prescribed acid-reducing medication
Days 3-7:
- Progress to full liquids (protein shakes, strained soups, low-fat milk)
- Most patients feel significantly better by day 3-4
- May return to desk work or light activities
- No heavy lifting or strenuous exercise
Weeks 2-3:
- Advance to soft/pureed foods (yogurt, scrambled eggs, mashed vegetables, soft fish)
- Small portions (2-4 tablespoons per meal)
- Continue prioritizing protein intake
- Light exercise can resume
Weeks 4-6:
- Gradual transition to solid foods
- Chew thoroughly; eat slowly
- Meals should be “side plate” size
- Normal activities including exercise fully resumed
Post-ESG Diet Progression
| Phase | Duration | Foods Allowed | Key Guidelines |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase 1: Clear Liquids | Days 1-2 | Water, broth, sugar-free drinks | 48-64 oz fluids daily; small sips |
| Phase 2: Full Liquids | Days 3-14 | Protein shakes, strained soups, milk | 60g protein daily minimum; no straws |
| Phase 3: Soft/Pureed | Weeks 3-4 | Yogurt, eggs, soft fish, mashed foods | Applesauce consistency; chew well |
| Phase 4: Regular Foods | Week 5+ | All foods (introduced gradually) | Protein first; small portions; avoid sugar |
Long-Term Lifestyle Guidelines
Eating Habits:
- Eat slowly; meals should take 20-30 minutes
- Chew each bite thoroughly (20+ chews)
- Stop eating at first feeling of fullness
- Avoid drinking during meals (wait 30 minutes after eating)
- Prioritize protein at every meal
Exercise:
- Begin light walking immediately post-procedure
- Resume full exercise by week 4-6
- Aim for 150+ minutes of activity weekly
- Include both cardio and strength training
Follow-Up Care:
- First follow-up: 1-2 weeks post-procedure
- Regular appointments: Monthly for first 3 months, then every 3 months
- Annual check-ups indefinitely
- Blood work to monitor nutritional status
ESG Cost by Country
ESG costs $4,500-$7,500 in Turkey compared to $9,000-$15,000 in the USA and £8,000-£12,000 in the UK, representing savings of 40-60% for the same FDA-approved procedure performed at internationally accredited facilities.
Price Comparison by Country
| Country | Price Range | Typically Includes |
|---|---|---|
| Turkey | €4,000-€7,000 / $4,500-$7,500 | All-inclusive: procedure, hospital, hotel, transfers, follow-up |
| United States | $9,000-$15,000 | Procedure only; facility and anesthesia fees often separate |
| United Kingdom | £8,000-£12,000 | Procedure and basic follow-up; limited package options |
| Germany | €8,000-€12,000 | Procedure and hospital fees |
| Mexico | $5,000-$8,000 | Variable package inclusions |
Why Prices Vary
Facility Costs: Operating room time, equipment, and hospital overhead represent major cost components. Countries with lower operating costs offer the same procedures at reduced prices.
Healthcare System Structure: The US healthcare system’s administrative complexity adds significant cost. Turkey’s medical tourism infrastructure is designed for efficiency and competitive pricing.
Device Costs: The OverStitch suturing device used in ESG has fixed costs globally, but overall pricing reflects local market conditions.
Inclusions: US and UK prices often cover only the procedure itself. Turkish all-inclusive packages incorporate accommodation, transportation, pre-operative testing, and extensive follow-up care.
Insurance Coverage
ESG insurance coverage remains limited in most countries:
- USA: Most private insurers do not cover ESG, though Medicare approved it for weight loss in adults. Some plans may cover when documented as medically necessary.
- UK: NHS coverage is extremely limited. Private health insurance (such as VitalityHealth) may cover ESG at select clinics.
- Turkey: Self-pay is standard for international patients, but the all-inclusive pricing often represents better value than out-of-pocket costs in Western countries.
How This Applies in Turkey
International guidelines from IFSO and ASMBS apply equally at Turkey’s JCI-accredited medical facilities, where ESG is performed using the same FDA-approved OverStitch device by board-certified specialists trained in advanced endoscopic bariatric techniques.
Turkey has emerged as a leading destination for ESG due to its combination of world-class medical infrastructure, experienced specialists, and cost-effective all-inclusive packages. Turkish hospitals serving international patients follow identical clinical protocols and safety standards as American and European institutions, with many surgeons having trained at leading Western centers.
The key advantages for international patients include significant cost savings of 40-60% compared to US/UK pricing, comprehensive packages that eliminate hidden fees, and streamlined timelines—most patients complete consultation, procedure, and initial recovery within 5-7 days versus months of waiting in countries with insurance requirements or NHS referral pathways.
At Carely Clinic in Istanbul, ESG is performed by board-certified gastroenterologists and bariatric surgeons at JCI-accredited partner hospitals. All-inclusive packages cover pre-operative testing, the procedure itself, hospital stay if needed, 4-5 star hotel accommodation, airport transfers, post-procedure follow-up, and 12-month remote monitoring support.
Learn more about Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty at Carely Clinic.
Summary: ESG vs Other Weight Loss Procedures
| Factor | ESG | Gastric Sleeve | Gastric Bypass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Procedure Type | Endoscopic (non-surgical) | Laparoscopic surgery | Laparoscopic surgery |
| Stomach Reduction | 70-80% (sutures) | 75-80% (removed) | ~80% + intestinal bypass |
| Weight Loss (1 Year) | 15-20% TBWL | 23-29% TBWL | 30-35% TBWL |
| Complication Rate | 1.5-2.3% | 12-18% | 15-20% |
| Hospital Stay | Same day (outpatient) | 1-2 nights | 2-3 nights |
| Return to Work | 2-3 days | 2-4 weeks | 2-4 weeks |
| Full Recovery | 4 weeks | 4-6 weeks | 6-8 weeks |
| Reversible | Yes (most cases) | No | No |
| GERD Risk | Low | Moderate-High | Low (may improve) |
| Ideal BMI Range | 30-40 | 35-50+ | 40+ |
| Cost (Turkey) | €4,000-€7,000 | €3,500-€5,500 | €5,000-€7,000 |
Frequently Asked Questions
How much weight will I lose with ESG?
ESG patients typically lose 15-20% of total body weight within one year, equivalent to 50-60% excess weight loss. Studies show 83% of patients achieve at least 10% total body weight loss by 12 months. Individual results depend on adherence to dietary guidelines, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications post-procedure.
Is ESG permanent?
Yes, ESG creates permanent stomach changes through sutures reinforced by scar tissue over 4-8 weeks. The stomach can gradually stretch if patients consistently overeat, potentially reducing effectiveness over years. Some patients may need suture reinforcement if significant stretching occurs, though 80% maintain results at 5 years.
How long does ESG last?
Five-year follow-up studies show patients maintain an average of 15.9% total body weight loss, with 90% keeping off at least 5% of their starting weight. Emerging 10-year data suggests durability extends well beyond five years when patients maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
Does ESG hurt?
No, ESG does not hurt during the procedure as you’re under general anesthesia. Post-procedure, most patients experience mild abdominal discomfort and nausea for 2-3 days managed with prescribed medications. Most patients report feeling significantly better by day 3-4, with pain levels much lower than surgical alternatives.
Can I have ESG if I had previous weight loss surgery?
In some cases, yes. ESG can be used to “revise” a stretched surgical gastric sleeve, helping patients who experienced weight regain restart their weight loss journey. However, patients with certain prior surgeries (gastric bypass, significant anatomical changes) are typically not candidates.
Is ESG covered by insurance?
No, most insurance does not cover ESG, though US Medicare approved it for adult weight loss in 2022. Most private US insurers and UK NHS provide no coverage, requiring self-pay. Turkish all-inclusive packages (€4,000-€7,000) often cost less than US out-of-pocket expenses ($9,000-$15,000), making medical tourism financially advantageous.
What is the ESG failure rate?
ESG has a 10-20% failure rate, meaning some patients don’t achieve significant weight loss or experience weight regain over time. Success depends on dietary adherence, regular follow-up attendance, exercise commitment, and psychological support. The procedure itself has over 98% technical success rate, with failures typically related to patient compliance rather than technique.
Can ESG be reversed?
Yes, ESG is reversible for most patients, particularly in the early weeks before scar tissue fully forms. The sutures can be endoscopically cut to restore normal stomach anatomy. This reversibility is a significant advantage over surgical procedures that permanently remove stomach tissue.
How soon can I exercise after ESG?
Light walking is encouraged immediately after the procedure to prevent blood clots. Most patients can resume full exercise routines, including strength training, within 4-6 weeks. There are no lifting restrictions like those required after abdominal surgery.
What happens if ESG doesn’t work?
Patients can undergo re-suturing to tighten the sleeve, combine ESG with GLP-1 medications, or convert to surgical bariatric procedures. Approximately 2.7% of ESG patients eventually convert to surgical gastric sleeve for insufficient weight loss. Re-suturing is performed endoscopically in 0.9% of cases when the stomach stretches or sutures loosen over time.
Is ESG safer than gastric sleeve surgery?
Yes, ESG has a significantly better safety profile. Serious complication rates are 1.5-2.3% for ESG versus 12-18% for surgical gastric sleeve. ESG has no reported mortality in major studies, causes minimal GERD, requires no incisions, and allows same-day discharge with faster recovery.
Who is the ideal candidate for ESG?
The ideal ESG candidate has BMI 30-40, failed previous diet/exercise attempts, prefers to avoid surgery, and can commit to permanent lifestyle changes. Patients should have no contraindications like large hiatal hernia or previous gastric surgery. ESG is particularly beneficial for Class I and II obesity patients who may not qualify for traditional bariatric surgery.
Conclusion
Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty represents a significant advancement in obesity treatment, offering meaningful and durable weight loss of 15-20% through a minimally invasive, incision-free approach with an excellent safety profile. The 2024 IFSO endorsement validates ESG as an effective treatment option, particularly for patients with Class I and II obesity who may not qualify for or prefer to avoid traditional surgery.
Key advantages include rapid recovery (2-3 days), minimal complications (1.5-2.3%), no permanent anatomical changes, and 5-year durability data showing maintained results. While surgical gastric sleeve achieves greater weight loss (23-29% vs 15-20%), ESG offers a dramatically safer risk profile that makes it appropriate for earlier intervention before obesity progresses.
For patients seeking a non-surgical path to significant weight loss, ESG provides a viable middle ground between lifestyle interventions and major surgery—achieving results that surpass diet and exercise alone while avoiding the risks, recovery time, and permanence of surgical options.
Individual requirements and outcomes vary. This guide provides general information based on international guidelines and peer-reviewed research. Consult with qualified medical professionals for personalized advice based on your specific health status and goals.
If you’re considering ESG and want to explore your options, our team can help assess your eligibility and provide detailed information about all-inclusive treatment packages in Turkey. Contact Carely Clinic for a free consultation.